Below are Various types of inheritance in Java.
1) Single Inheritance
Single inheritance is damn easy to understand. When a class extends another one class only then we call it a single inheritance. The below flow diagram shows that class B extends only one class which is A. Here A is a parent class of B and B would be a child class of A.
Single Inheritance example program in Java
class Teacher { String designation = "Teacher"; String collegeName = "Studywithbs"; void does(){ System.out.println("Teaching"); } } public class PhysicsTeacher extends Teacher{ String mainSubject = "Physics"; public static void main(String args[]){ PhysicsTeacher obj = new PhysicsTeacher(); System.out.println(obj.collegeName); System.out.println(obj.designation); System.out.println(obj.mainSubject); obj.does(); } }
Output:
Studywithbs Teacher Physics
Teaching
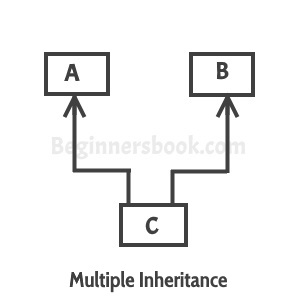
2) Multiple Inheritance
“Multiple Inheritance” refers to the concept of one class extending (Or inherits) more than one base class. The inheritance we learnt earlier had the concept of one base class or parent. The problem with “multiple inheritance” is that the derived class will have to manage the dependency on two base classes.
Note 1: Multiple Inheritance is very rarely used in sofware projects. Using Multiple inheritance often leads to problems in the hierarchy. This results in unwanted complexity when further extending the class.
Note 2: Most of the new OO languages like Small Talk, Java, C# do not support Multiple inheritance. Multiple Inheritance is supported in C++.
But we can access Multiple Inheritance in java by using interfaces.
interface X { public void myMethod(); } interface Y { public void myMethod(); } class JavaExample implements X, Y { public void myMethod() { System.out.println("Implementing more than one interfaces"); } public static void main(String args[]){ JavaExample obj = new JavaExample(); obj.myMethod(); } }
Output:
Implementing more than one interfaces
3) Multilevel Inheritance
Multilevel inheritance refers to a mechanism in OO technology where one can inherit from a derived class, thereby making this derived class the base class for the new class. As you can see in below flow diagram C is subclass or child class of B and B is a child class of A. For more details and example refer – Multilevel inheritance in java with example program.
Multilevel Inheritance example program in Java
Class X { public void methodX() { System.out.println("Class X method"); } } Class Y extends X { public void methodY() { System.out.println("class Y method"); } } Class Z extends Y { public void methodZ() { System.out.println("class Z method"); } public static void main(String args[]) { Z obj = new Z(); obj.methodX(); //calling grand parent class method obj.methodY(); //calling parent class method obj.methodZ(); //calling local method } }
4) Hierarchical Inheritance
In such kind of inheritance one class is inherited by many sub classes. In below example class B,C and D inherits the same class A. A is parent class (or base class) of B,C & D. Read More at – Hierarchical inheritance in java with example program.
class A { public void methodA() { System.out.println("method of Class A"); } } class B extends A { public void methodB() { System.out.println("method of Class B"); } } class C extends A { public void methodC() { System.out.println("method of Class C"); } } class D extends A { public void methodD() { System.out.println("method of Class D"); } } class JavaExample { public static void main(String args[]) { B obj1 = new B(); C obj2 = new C(); D obj3 = new D(); //All classes can access the method of class A obj1.methodA(); obj2.methodA(); obj3.methodA(); } }
Output:
method of Class A method of Class A method of Class A
5) Hybrid Inheritance
In simple terms you can say that Hybrid inheritance is a combination of Single and Multiple inheritance. A typical flow diagram would look like below. A hybrid inheritance can be achieved in the java in a same way as multiple inheritance can be!! Using interfaces. yes you heard it right. By using interfaces you can have multiple as well as hybrid inheritance in Java.
Hybrid inheritance in java with example program.
class C { public void disp() { System.out.println("C"); } } class A extends C { public void disp() { System.out.println("A"); } } class B extends C { public void disp() { System.out.println("B"); } } class D extends A { public void disp() { System.out.println("D"); } public static void main(String args[]){ D obj = new D(); obj.disp(); } }
Output:
D





0 Comments
Post a Comment